Overview of the advanced electronic signature
Despite the ongoing digital transformation, documents are still signed by hand on paper in 2025. However, this approach often leads to increased bureaucracy, is time-consuming and cost-intensive and has proven to be inefficient. More and more companies are therefore making use of the possibilities offered by electronic signatures.
In this article you will learn how documents can also be signed digitally, what types of electronic signatures exist, what advantages the e-signature offers in practice and why the advanced electronic signature has proven itself in the business environment.
What is an advanced electronic signature?
The advanced electronic signature is a central component of the digital transformation and enables documents to be signed electronically in a secure and verifiable manner. An important prerequisite for the advanced electronic signature is that the signatory of the document can be clearly identified. To achieve this, the signature data is inseparably linked to the document. In addition, it is ensured that the document cannot be changed undetected once it has been signed. This is also known as document integrity.

The advanced electronic signature offers a high level of security. It is estimated that around 95% of digitally signed documents in day-to-day business are signed with an advanced electronic signature.
Requirements for an advanced electronic signature
What an advanced electronic signature must fulfil in detail in order to be legally recognized is clearly regulated. The European Union has published its own regulation (910/2014) for this purpose. The “Electronic Identification and Trust Services for Electronic Transactions” regulation, or short eIDAS, defines 4 key requirements:

1
Unique assignment to the signatory: The signature must be clearly assigned to the signatory
2
Identification of the signatory: It must enable the signatory to be identified.
3
Electronic signature creation data under the sole control of the signatory: It is created by means that the signatory can keep under his sole control.
4
Integrity of the document: It is linked to the signed data in such a way that any subsequent change to the data can be recognized.
The advanced electronic signature in practice
Even if the regulation may sound complicated at first, the use of the advanced electronic signature is simple in practice. Various providers, such as the company StepOver, offer solutions for advanced electronic signatures. These solutions can also be easily integrated into existing company processes.
Handwritten electronic signatures on a signature pad are frequently used. This form is used particularly for face-to-face processes, such as counter-to-cashier situations. The advantage: signing on a signature pad is similar to signing on paper and thus creates a high level of acceptance among the signatories.

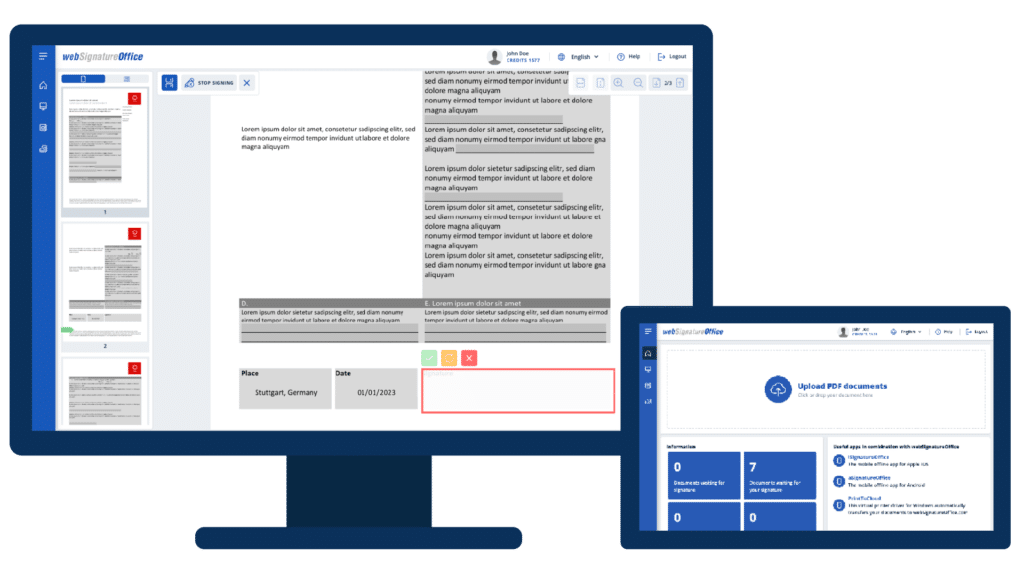
With the help of online signature solutions such as webSignatureOffice, signatures can also be obtained from people who are in a different location. The signatory then receives a link by email which they can use to conveniently sign the document on their smartphone, tablet or PC. In the online process, other unique identifiers such as the signatory’s email address and telephone number are often used to identify the signatory in addition to the signature’s biometric data. This is also recognized as an advanced electronic signature.
The three different forms of electronic signature
According to the eIDAS Regulation, there are three different forms of electronic signature.
1
The simple electronic signature: According to Art. 3 of the “eIDAS Regulation”, electronic signatures are data in electronic form which are attached to or logically associated with other electronic data, which the signatory uses to sign. This could, for example, be a scanned signature with a name in a document. Normally, the evidential value of such a simple electronic signature is rather low. For this reason, it is mainly used by companies for internal communication.
2
The advanced electronic signature, on the other hand, offers a very high evidential value, as it ensures that the document cannot be changed without being recognized after it has been signed. The signature can be assigned to the signatory and uniquely identifies them. This makes the advanced electronic signature the most commonly used signature form in the business environment.
3
The qualified electronic signature also requires the signatory to be identified by a so-called trust service provider using, for example, a video identification procedure. The qualified electronic signature is more complex than the advanced electronic signature and is only required if national legislation makes it mandatory for certain transactions (e.g. in Germany, if the written form is required). The qualified electronic signature has the highest evidential value.
Advantages of the advanced electronic signature
-
Time savings and increased efficiency: By using the advanced electronic signature, contracts can be concluded in real time, eliminating time-consuming intermediate steps such as printing and scanning. This speeds up business processes considerably and increases efficiency.
-
Independence of time and place: Advanced electronic signatures make it possible to sign documents regardless of time and place. This is particularly advantageous for remote work or international business relationships, as signatories do not need to be physically present.
-
Sustainability and cost savings: Eliminating paper and printing materials reduces a company’s ecological footprint. It also eliminates costs for paper, printers, ink and postage, resulting in considerable savings.
-
Legal validity and security: According to the eIDAS Regulation, electronic signatures must be admissible as evidence in court in the EU and can therefore be used in most business cases instead of handwritten signatures. They also offer a high level of security against tampering thanks to encryption technologies and checksums and increase the probative value of electronically archived documents compared to simple scans.
-
Modernization and competitiveness: The introduction of electronic signatures positions companies as progressive and innovative. This can strengthen customer loyalty and create a competitive advantage.
-
Optimization of internal processes: Digitizing signature processes streamlines internal workflows. This leads to better organization and allows employees to focus on value-adding activities.

